Strokes are brain attacks. They occur when the blood supply to the brain becomes blocked. A stroke is a medical emergency that needs immediate medical attention. A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of your brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. 80% of the strokes are ISCHEMIC STROKE, means they are caused by A BLOOD CLOT and 20% strokes are HEMORRHAGIC STROKES, means they are caused by BLEEDING IN THE BRAIN and A TRANSIENT ISCHEMIC ATTACK(TIA) also known as a MINI STROKE. In this medical condition, quickness is very much required. The more quickly a person gets treatment, the less quickly patient’s brain tissue will likely to damage permanently. For a person experiencing a stroke to get the best diagnosis and treatment possible, they should be treated at a hospital within 3 hours of their symptoms first appearing.
Let’s go through the types of STROKES:
Ischemic stroke
About 80 percent of strokes are ischemic strokes. Ischemic strokes occur when the arteries to your brain become narrowed or blocked, causing severely reduced blood flow (ischemia).
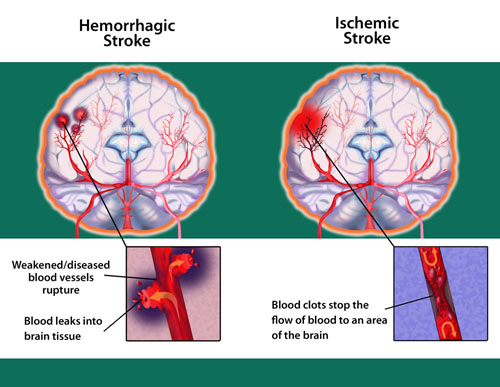
Hemorrhagic stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in your brain leaks or ruptures. Brain hemorrhages can result from many conditions that affect your blood vessels.
Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) — sometimes known as a ministroke — is a temporary period of symptoms similar to those you’d have in a stroke. A temporary decrease in blood supply to part of your brain causes TIAs, which may last as little as five minutes.
Like an ischemic stroke, a TIA occurs when a clot or debris blocks blood flow to part of your nervous system — but there is no permanent tissue damage and no lasting symptoms.
Signs of STROKE:
- Trouble seeing or blurry vision- A stroke can blur the vision or can double the vision.
- Difficulty in speaking and Confusion- A stroke can make a person confused while speaking even a single word. It can make the person use wrong words or become completely unable to speak. Confusion, including trouble with speaking and understanding.
- Weakness- During stroke, it is very evident that one or both legs or arms may suddenly become paralyzed or go weak or numb. Numbness or inability to move parts of the face, arm, or leg, particularly on one side of the body.
- Dizziness- Sudden dizziness or loss of balance can signal a stroke.
- Pain- In stroke, mild pain and then sudden intense pain occurs in one leg or arm or on one side or other side of face or chest.
- Severe Headache – The pain is too intense to bear. It felt as if this could be the worse pain ever happened and in women this pain starts early as a sign of stroke than men. A headache, possibly with altered consciousness or vomiting
- Face Drooping- Sudden, one-sided weakness, sagging, or paralysis in the face could mean a person is having stroke.
- Fatigue- Women are more likely to feel fatigue and discomfort in their body than man as a sign of stroke.
- Hiccups- Hiccups can also be a sign of stroke if it goes on in continuity for long time.
- Shortness in Breath- Breathlessness or shortness in breath can also be a cause of stroke.
CAUSES OF STROKE:
- High blood pressure (Hypertension)
- High cholesterol,
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Central Obesity
- A type of irregular heartbeat known as atrial fibrillation (AF)
- Poor diet and Inadequate physical activity
PREVENTION:
There are some risk factors, such as age, gender, and family history, that can’t be changed. However, there are some risk factors that can be addressed with lifestyle changes and/or medicines to help prevent stroke.
Treating risk factors
- Visit your doctor regularly for blood pressure checks and appropriate medication.
- Have your cholesterol checked – your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes or medicines to lower your cholesterol.
- Control your diabetes, if you have it.
Lifestyle changes that can help reduce your risk of stroke include:
- Stopping smoking;
- Eating a healthy diet (a diet that is high in vegetables and fruit, and low in salt and saturated and trans fats is recommended);
- Losing weight if you are overweight;
- Reducing alcohol intake
- Getting enough physical activity (at least 30 minutes on most days of the week).
Recovery from STROKE:
Recovery time after a stroke is different for everyone—it can take weeks, months, or even years. Some people recover fully, but others have long-term or lifelong disabilities.
What to Expect After a Stroke
If you have had a stroke, you can make great progress in regaining your independence. However, some problems may continue:
- Paralysis (inability to move some parts of the body), weakness, or both on one side of the body.
- Trouble with thinking, awareness, attention, learning, judgment, and memory.
- Problems understanding or forming speech.
- Trouble controlling or expressing emotions.
- Numbness or strange sensations.
- Pain in the hands and feet that worsens with movement and temperature changes.
- Trouble with chewing and swallowing.
- Problems with bladder and bowel control.
- Depression.
Stroke Rehabilitation
Rehab can include working with speech, physical, and occupational therapists.
- Speech therapy helps people who have problems producing or understanding speech.
- Physical therapy uses exercises to help you relearn movement and coordination skills you may have lost because of the stroke.
- Occupational therapy focuses on improving daily activities, such as eating, drinking, dressing, bathing, reading, and writing.
Therapy and medicine may help with depression or other mental health conditions following a stroke. Joining a patient support group may help you adjust to life after a stroke. Talk with your health care team about local support groups, or check with an area medical center.
Support from family and friends can also help relieve fear and anxiety following a stroke. Let your loved ones know how you feel and what they can do to help you.
